The history of dry pasta as we know it today is linked to the Arab domination of Sicily according to various historians
It was 1154, when the Arab geographer Edrisi mentioned “a food of flour in the form of threads”, the “triyah” prepared in Trabia. From Sicily, the pasta thus prepared was then exported to the continent.
Again according to the Arab geographer, already in the mid-1100s in Sicily, and in particular in the Trabia area, "so much pasta" was produced that it was exported "to all parts, to Calabria and to other Muslim and Christian countries and many shiploads of it were sent".
But how good is pasta, how can you do without it?
This is the question we often ask ourselves but let's face it, pasta is good for you.

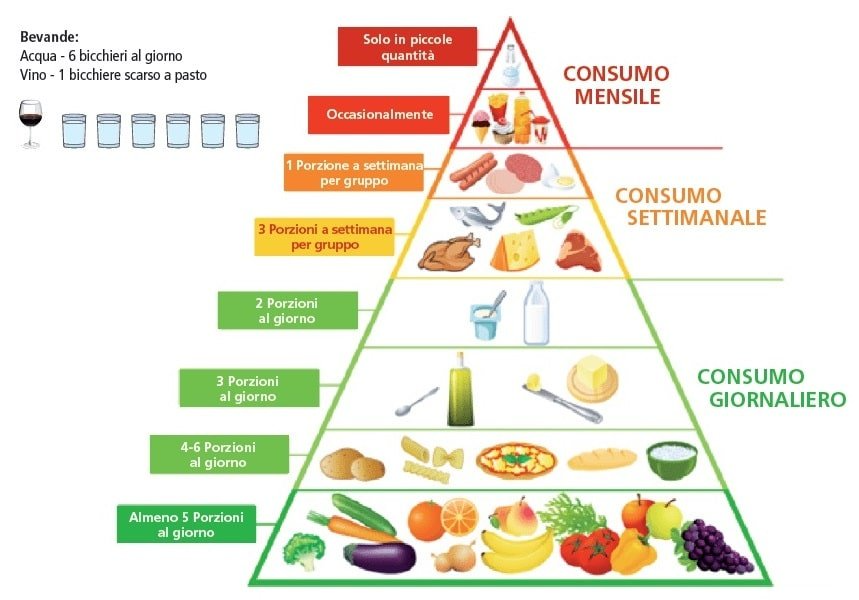
Pasta is the basis of a healthy diet
A cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, Pasta should be considered an essential food in your daily diet.
With its high content of complex carbohydrates, Pasta is to be considered a particularly important food in our diet.
In the graphic representation of the food pyramid, cereals rich in complex carbohydrates, including pasta, are placed at the base, where foods that should be consumed several times a day are located.
Pasta also contains a fair amount of proteins (around 11%), although with low biological value, while it has a completely negligible amount of fat.
The pasta and the sport
Pasta nello Sport is a typical food of our Italian tradition and occupies a place of honor in the food pyramid of the Mediterranean diet.
From an energy point of view, semolina pasta provides approximately 350 Kcal per 100g, while wholemeal pasta provides 320 Kcal and egg pasta provides 365 Kcal.
In an endurance sport such as cycling, marathon, triathlon or any other resistance sport, the presence of pasta in the athlete's weekly diet is fundamental.
But if you are not a sports professional, it makes little difference, pasta is recommended in the diet of those who want to stay in good health, but also for those who want to lose a little weight (satiating property of Pasta, especially wholemeal) and for those who, having to perform intense physical activity, need readily usable energy. Furthermore, if taken together with protein foods (fish, meat or cheese based condiment) it allows you to use proteins for plastic purposes (to promote muscle growth), rather than energy.


Pasta and Children
A healthy and balanced diet is essential for the growth of children.
In fact, it cannot ignore the nutritional contribution of bread and pasta (preferably wholemeal), fruit and vegetables, legumes, fish and meat.
Pasta and cereals should even be consumed both at lunch and dinner: this food represents a fundamental component of their diet.
Pasta is very important and it is so above all for one reason: it represents the primary energy source of carbohydrates essential for physical activity and the consequent development of the body.
Experts speak out
We asked Dr. Valentina Schirò, a nutritional biologist and specialist in food science, to address the following topics:
- Pasta and Sports
- Pasta and Diet
- Pasta and Pathologies
- Pasta e Fake News
Thanks to his experience and knowledge, we have prepared the document "A journey to discover Sicilian pasta and nutrition" that you can download via the following button.